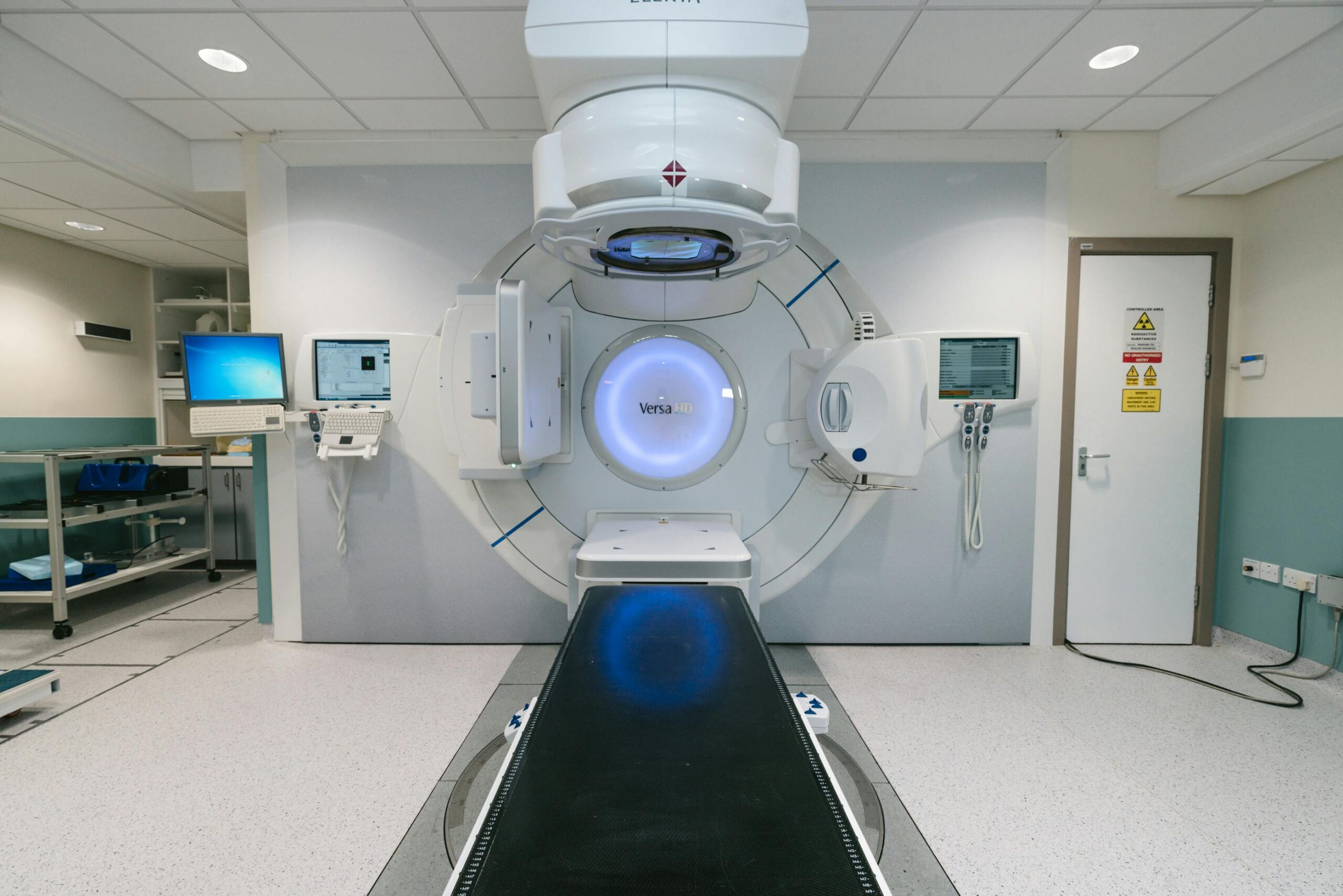
08 Oct Innovative Techniques in Radiation Therapy Delivery
Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses beams of intense energy to kill cancer cells, and it is used to target tumors that cannot be removed surgically. The goal of this treatment is to damage the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from growing and dividing. Radiation may be delivered externally via a machine or internally with radioactive material placed inside the body. Here is more information about innovative techniques in this field:
Intensity-modulated Radiation Therapy
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) uses multiple small radiation beams of varying intensities to conform to the shape of a tumor. The beams are delivered from many different angles, and doctors adjust them to deliver a higher dose to the cancer. This precision enables more effective treatment of tumors near sensitive areas. Benefits may include:
- Delivers precise doses of radiation to the tumor.
- Aims to minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissues and organs.
- May reduce the risk of side effects compared to traditional methods.
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) delivers very high doses of radiation to a tumor in a few treatment sessions. Because the dose is precise, SBRT is an option for tumors in many parts of the body. Medical physicists and radiation oncologists work together to plan the treatment and accurately target the cancer.
Image-guided Radiation Therapy
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) uses frequent imaging during a course of radiation treatment to improve the precision of delivery. Tumors may move between treatments, so IGRT adjusts the patient’s position or the radiation beams to account for these changes. Built directly into the treatment machine, advanced imaging technologies such as CT scans or X-rays provide real-time guidance.
This technique tracks tumor motion caused by bodily functions such as breathing. The process typically involves taking images of the tumor, which allows the radiation oncologist to make immediate adjustments. This level of accuracy helps to minimize radiation exposure to healthy tissues surrounding the cancer.
The use of IGRT allows clinicians to deliver radiation with a high degree of precision. Different imaging methods offer specific advantages for various tumor sites, and the selection of the imaging technique is customized to the individual patient’s case. This personalization enhances the delivery of the planned radiation dose throughout treatment.
Volumetric Arc Therapy
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is an advanced form of IMRT that delivers radiation in a continuous arc as the treatment machine rotates around the patient. This method enables a highly sculpted three-dimensional dose distribution, and it may shorten treatment times significantly compared to conventional techniques. The treatment machine’s rotation speed, beam shape, and dose rate typically change continuously during the therapy session.
3D and 4D CRT Therapy
Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) uses imaging scans to create a detailed, three-dimensional representation of the tumor and surrounding organs. Providers then shape and aim radiation beams from several directions to match the tumor’s specific shape, which may reduce radiation damage to healthy tissue. This technique is a fundamental approach in modern radiation oncology, and it plays a key role in treatment procedures.
Four-dimensional CRT (4D-CRT) adds the element of time to 3D-CRT. It accounts for tumor motion from processes like respiration by tracking the tumor through the breathing cycle. Both therapies may be available, and they could be offered depending on the patient’s needs.
Schedule Radiation Sessions Today
Advanced techniques are available for treating various types of cancer. These methods are designed to target tumors with precision while managing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. Speak with a oncologist to learn about radiation options and schedule an appointment.

No Comments